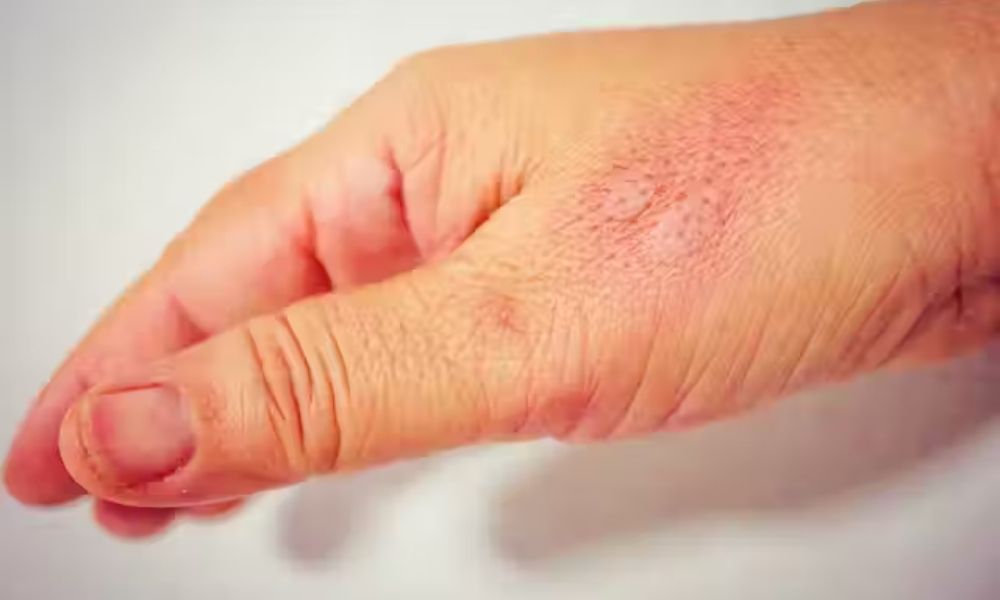
Inflammation is a natural response of the body’s immune system to injury, infection, or irritation. It is a complex process that involves various cells, chemicals, and signaling pathways. While inflammation is often associated with negative effects such as pain, redness, and swelling, it actually plays a crucial role in protecting the body and promoting healing. In this article, we will explore the immunological benefits of inflammation and how it helps the body fight against diseases.
Contents
What is Inflammation?
Inflammation is the body’s response to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. It is a protective mechanism that aims to remove the cause of injury or infection and initiate the healing process. The process of inflammation involves a series of events that are triggered by the immune system.
When the body detects a threat, it releases chemicals called cytokines, which act as messengers to alert the immune system. These cytokines cause blood vessels to dilate, allowing more blood to flow to the affected area. This results in redness, warmth, and swelling. The increased blood flow also brings more white blood cells to the site of injury or infection, which helps to fight off any pathogens or foreign substances.
Read:What are the benefits of pink himalayan salt?Inflammation can be acute or chronic. Acute inflammation is a short-term response that lasts for a few days or weeks and is usually triggered by an injury or infection. On the other hand, chronic inflammation is a long-term response that can last for months or even years. It is often caused by autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis, or lifestyle factors, such as obesity and smoking.
The Immunological Benefits of Inflammation
While inflammation is often associated with negative effects, it actually plays a crucial role in the body’s immune response. Here are some of the immunological benefits of inflammation:
- Elimination of pathogens: One of the primary functions of inflammation is to eliminate pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi. When the body detects a pathogen, it triggers an inflammatory response to contain and destroy it. The increased blood flow and white blood cells help to fight off the infection and prevent it from spreading to other parts of the body.
- Activation of the immune system: Inflammation also helps to activate the immune system and prepare it to fight against future infections. When the body is exposed to a pathogen, it produces antibodies that specifically target that pathogen. These antibodies remain in the body and provide long-term protection against the same pathogen. Inflammation helps to activate the production of these antibodies, making the body more resistant to future infections.
- Removal of damaged cells: Inflammation also plays a crucial role in removing damaged or dead cells from the body. When cells are damaged due to injury or infection, they release chemicals that attract white blood cells to the site of injury. These white blood cells then engulf and remove the damaged cells, allowing new healthy cells to take their place.
- Promotion of tissue repair: Inflammation also promotes tissue repair by stimulating the production of new blood vessels and connective tissue. This helps to bring essential nutrients and oxygen to the site of injury, which is crucial for the healing process. Inflammation also helps to remove debris and dead cells from the site of injury, allowing new tissue to grow and repair the damaged area.
Examples of Inflammation in Action
To better understand the immunological benefits of inflammation, let’s look at some real-life examples of how it helps the body fight against diseases:
Read:What are the benefits of pineapple- Wound healing: When you get a cut or a scrape, the body triggers an inflammatory response to protect the wound from infection. The increased blood flow and white blood cells help to clean the wound and remove any foreign substances. The inflammation also helps to stimulate the production of new cells and tissues, allowing the wound to heal.
- Infection control: Inflammation is also crucial in controlling and eliminating infections. For example, when you get a cold or the flu, your body triggers an inflammatory response to fight off the virus. The increased mucus production and coughing are all part of the body’s attempt to remove the virus from the respiratory tract.
- Autoimmune disorders: While chronic inflammation is often associated with negative effects, it actually plays a crucial role in autoimmune disorders. In these conditions, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells and tissues, causing inflammation. While this can lead to tissue damage, it also helps to remove the damaged cells and promote tissue repair.
The Link Between Inflammation and Chronic Diseases
While acute inflammation is a necessary and beneficial response, chronic inflammation can have negative effects on the body. Studies have shown that chronic inflammation is linked to various chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
Read:What are the benefits of taking creatine?Chronic inflammation can occur when the body’s immune system is constantly activated due to factors such as obesity, smoking, and stress. This can lead to a continuous cycle of inflammation, which can damage healthy cells and tissues and increase the risk of chronic diseases.
For example, chronic inflammation in the arteries can lead to the formation of plaques, which can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. Inflammation in the pancreas can also lead to insulin resistance, which is a precursor to type 2 diabetes. Inflammation has also been linked to the development of certain types of cancer, such as colon and lung cancer.
How to Reduce Inflammation in the Body
While inflammation is a natural and necessary response, chronic inflammation can have negative effects on the body. Therefore, it is essential to keep inflammation under control to maintain good health. Here are some ways to reduce inflammation in the body:
- Eat a healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can help to reduce inflammation in the body. These foods are rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds that can help to neutralize free radicals and reduce inflammation.
- Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity can help to reduce inflammation in the body. Exercise helps to improve blood flow and stimulate the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can lead to increased inflammation in the body. Therefore, it is essential to find ways to manage stress, such as practicing relaxation techniques, getting enough sleep, and engaging in enjoyable activities.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can increase inflammation in the body. Therefore, it is essential to limit or avoid these habits to maintain good health.
The Bottom Line:
Inflammation is a natural and necessary response of the body’s immune system. While it is often associated with negative effects, such as pain and swelling, it plays a crucial role in protecting the body and promoting healing. Inflammation helps to eliminate pathogens, activate the immune system, remove damaged cells, and promote tissue repair. However, chronic inflammation can have negative effects on the body and is linked to various chronic diseases. Therefore, it is essential to keep inflammation under control through a healthy lifestyle and proper management of chronic conditions.
By understanding the immunological benefits of inflammation, we can appreciate its role in maintaining good health and take steps to keep it in balance. So the next time you experience inflammation, remember that it is your body’s way of protecting and healing itself.